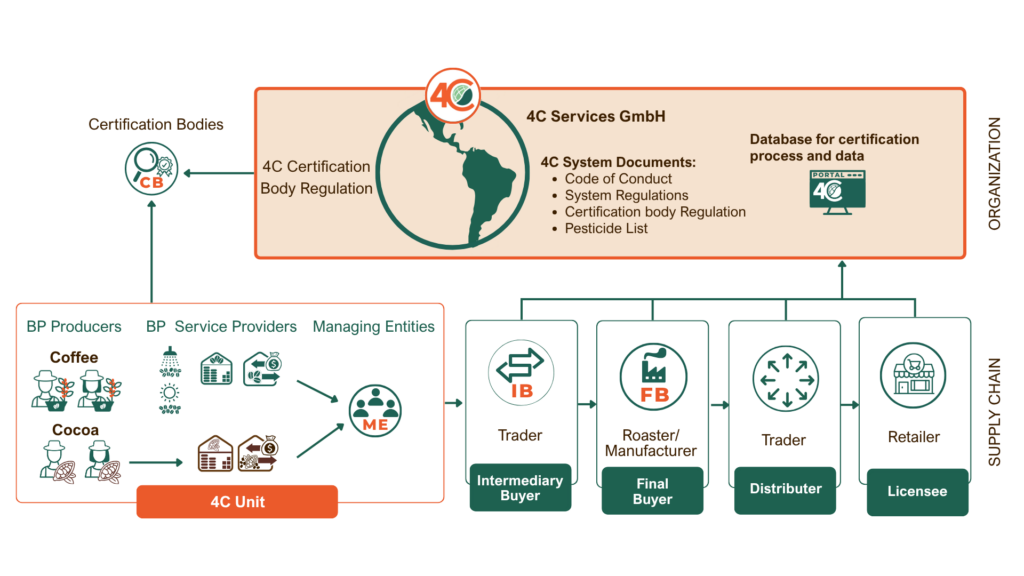
Our System
4C System Users
4C System Users Overview
List of active 4C System Users and Certificates

Independent Auditors
Certification Bodies
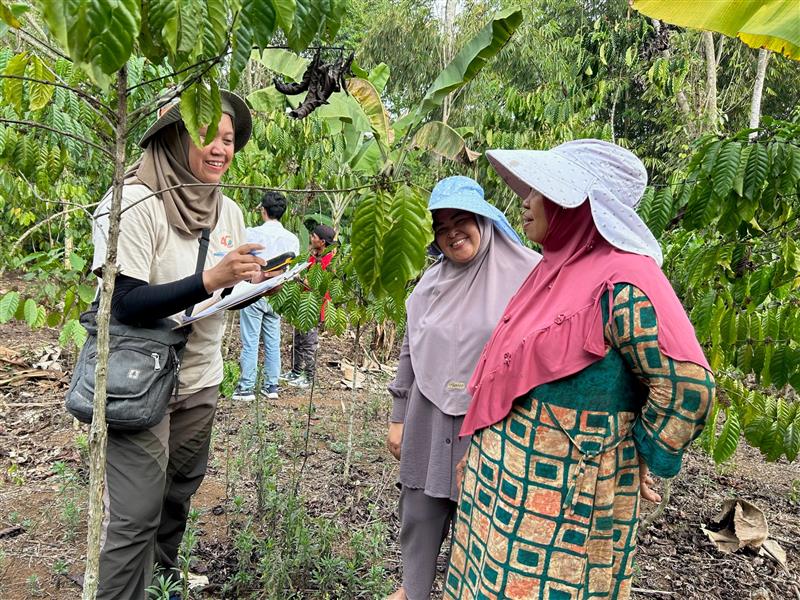
4C is a third-party certification system working with independent, accredited auditors. In the 4C System, these auditors, known as Certification Bodies (CBs), play a crucial role, as they conduct all 4C audits. The only exception is the 4C Integrity audits, which fall under the scope of the 4C Integrity Program.
Certified Producer Groups
4C Unit
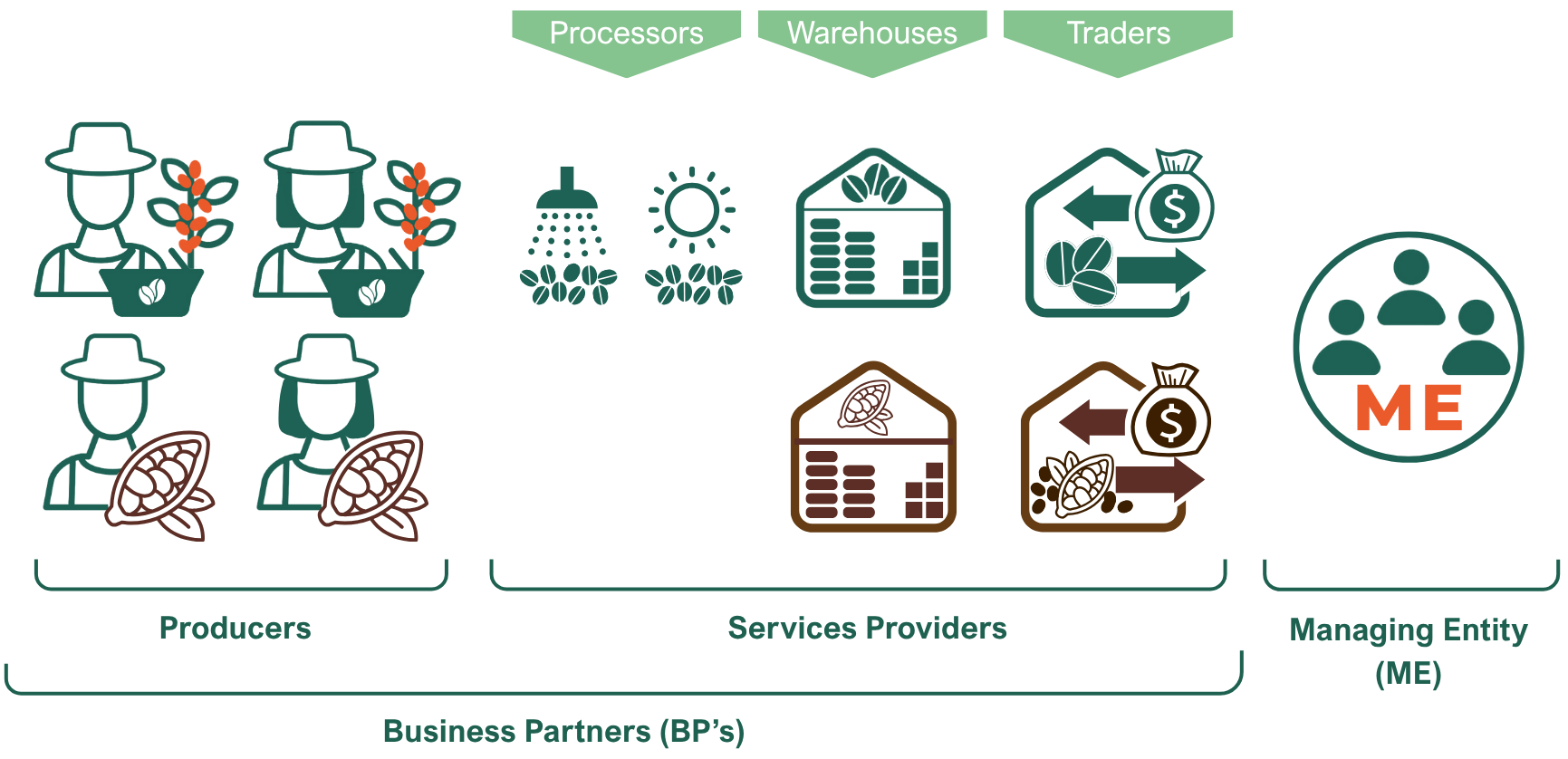
Producer groups with 4C certified agricultural products are called the 4C Unit. These groups include any type of production and process facilities that produce a minimum of 20 tonnes of 4C certified green coffee or cocoa bean per year. They consist of the Managing Entity (ME) and its Business Partners (BPs).
Managing Entity (ME)
The Managing Entity is a legally registered person, company, or organisation that administers its 4C Unit. As the certificate holder, the ME is responsible for ensuring compliance with 4C requirements within its 4C Unit.
What are the responsibilities of the Managing Entity?
The Managing Entity (ME):
Organises its 4C Unit; that is, it defines its Business Partners (BPs) to be listed in the Business Partner Map (BPM) and updates this BPM regularly.
Establishes contact with the Certification Body to initiate (re)certification and to ensure that an existing 4C certificate is maintained.
Ensures the implementation of requirements within its 4C Unit and compliance by all of its Business Partners (BPs). This includes, for example, establishing the traceability system and the Internal Management System (IMS) of the 4C Unit.
Business Partner Producers (BP Producers)
BP Producers are either natural persons (farmers) or legally registered entities (farms) that grow coffee or cocoa. 4C differentiates between regular BP Producers and smallholders (a definition of which can be found in the 4C System Regulations).
Business Partner Service Providers (BP Service Providers)
BP Service Providers are either natural persons or legally registered entities that provide services such as trading, storage, and/or processing within the 4C Unit. Depending on their role, BP Service Providers may include local traders, warehouses, and wet or dry mills. They may operate as independent facilities or as subbranches of the Managing Entity (ME).

Intermediaries
Intermediary Buyers
In most supply chains, there are intermediaries – such as exporters, importers, traders, processors, or other entities involved in the trading of products. In the 4C System, these are referred to as Intermediary Buyers (IBs) and are permitted to trade 4C certified products outside of producer organisations (4C Units).
Intermediary Buyers may also obtain certification under the Chain of Custody certification scheme.
End-of-Chain Companies
Final Buyers
The final actors in the supply chain of 4C-certified raw agricultural products – such as coffee roasters, cocoa processors, and manufacturers – are referred to as Final Buyers. To ensure responsible trade, Final Buyers sign the Final Buyer Agreement and comply with its provisions when purchasing and selling 4C-certified products.


Resellers
Distributors
After the raw product has been processed, companies may purchase it from the Final Buyer for onward sale to, for example, retailers. In the 4C System, these companies are referred to as Distributors and are permitted to trade 4C-certified products after processing. An Intermediary Buyer may also act as a Distributor.
Distributors may also obtain certification under the Chain of Custody certification scheme.
Brands and Retailers
Licensees
At the end of the supply chain are the organisations that sell directly to consumers, such as retailers, brand owners, and coffee shops. In the 4C System, these actors are known as Licensees. As Licensees, they are authorised to make both on-pack and off-pack claims for 4C certified products.
Registration as a 4C Licensee is only required if the company is not already registered as a Final Buyer.

Learn more about key terms, definitions, and concepts in our 4C Academy.

If you would like to find out how to obtain the 4C certification for coffee or cocoa production.